
How To Choose Between Fixed and Variable Interest-Rate?
Many borrowers face the challenge of deciding between variable interest rate and the fixed interest rates. So, if you are not sure of the choice that you should opt for, our article will guide you on the two options, together with their pros and cons to help you make an informed decision. Both options are good, especially when applied correctly on different types of loans depending on the borrower’s preferences.

 To illustrate this more clearly, assume that the bank gives the borrower $300,000, 30-year loan with an introductory rate of 3.5% and a 5/1 ARM. The borrower will pay $1,347 monthly for the first five years. After that period, the remaining debt will be paid on fluctuating rates which will depend on the interest rates set by the benchmark indexes.
If the rates increase by 6%, for instance, the borrower will make monthly payments of $1,347. However, if the rates reduce by 3%, the borrower will pay $1,265. On the other hand, if the borrower opts for the fixed interest rate option, he or she will make equal monthly payments of $1,347 for 30 years.
To illustrate this more clearly, assume that the bank gives the borrower $300,000, 30-year loan with an introductory rate of 3.5% and a 5/1 ARM. The borrower will pay $1,347 monthly for the first five years. After that period, the remaining debt will be paid on fluctuating rates which will depend on the interest rates set by the benchmark indexes.
If the rates increase by 6%, for instance, the borrower will make monthly payments of $1,347. However, if the rates reduce by 3%, the borrower will pay $1,265. On the other hand, if the borrower opts for the fixed interest rate option, he or she will make equal monthly payments of $1,347 for 30 years.
Before settling on a specific option, look at:
While some lenders and financial advisors might advise you to use a specific rate depending on the market behavior, you should focus more on your repayment ability to avoid getting yourself in a bad financial situation. You should also carry out enough research to find out different lenders are offering, their terms and conditions, and their rates so that you can choose the best.
Fixed Interest Loan Rate
Fixed interest is an interest rate that does not fluctuate during the loan repayment period. It allows the borrower to make predictions on how they will make their future repayments.Characteristics
The fixed interest rate is usually based on the lender’s assumptions in regards to the average discount rate for a specified period. For instance, if the discount rate is low, the fixed rates usually are higher than the variable rates because the interest rates might rise during the fixed period. Since the rates remain the same throughout the loan period, a fixed interest rate loan is attractive to the borrowers who will not want the interest rates to rise or fall during the repayment period. A financially stable household mostly uses fixed interest rates because they have a consistent flow of income. Fixed rates are also applied in other loans which have a more extended repayment period.Main Advantage
You will be able to plan your finances better when using the fixed interest rate plan because you already know what to pay, and when to pay. You will also have proper budgeting.Main Disadvantages
As compared to the variable loan rates, you may end up paying more when using this plan.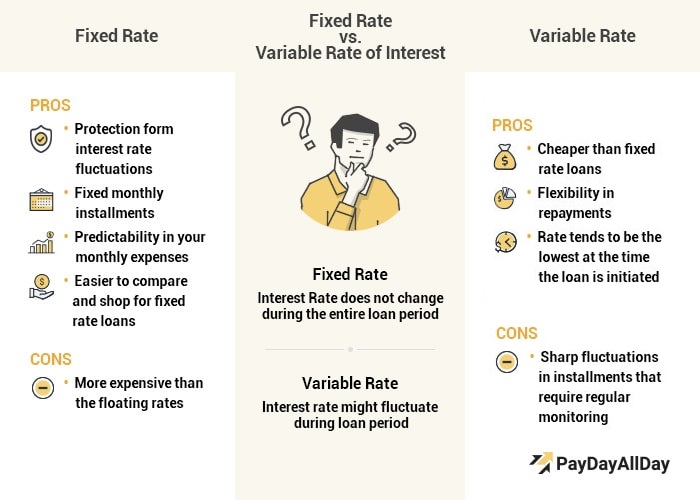
Variable Interest Rates
A variable interest rate for a loan is a rate which fluctuates over time. It is generally based on the market conditions as well as the benchmark index set but the federal authorities.Characteristics
It means that the interest rates increases when the underlying index increases, and reduces when the overall index reduces. The underlying benchmark index primary depends on the loan type or the collateral given for the loan. Variable interest rates are ideal to the small households which do not have a consistent flow of income. They are also used in student loans and all types of loans which have a short repayment period.Main Advantage
Flexibility is the main asset in the variable interest rates plan. You don’t have to worry about getting penalties if you don’t deliver a defined set repayment amount. Additionally, you can decide to pay more if you have the money, and by so doing, you will settle your loan faster.Main Disadvantage
Lack of predictability is seen as a disadvantage as you can’t predict the future, and so you can’t know what will happen tomorrow, and what you will pay. It often leads to poor planning. More to that, sometimes the interest rates can be higher than what you can afford.Difference Between Fixed And Variable Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates have a constant loan repayment amount while the variable rates have fluctuating rates. For instance, if the borrower gets an adjustable rate loan, he or she will receive an introductory rate for a certain period, often for less than five years. Once that period elapses, the rates will start to fluctuate on a periodic basis as determined by the lender.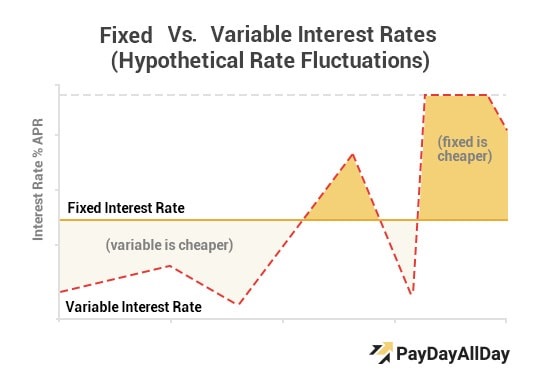 To illustrate this more clearly, assume that the bank gives the borrower $300,000, 30-year loan with an introductory rate of 3.5% and a 5/1 ARM. The borrower will pay $1,347 monthly for the first five years. After that period, the remaining debt will be paid on fluctuating rates which will depend on the interest rates set by the benchmark indexes.
If the rates increase by 6%, for instance, the borrower will make monthly payments of $1,347. However, if the rates reduce by 3%, the borrower will pay $1,265. On the other hand, if the borrower opts for the fixed interest rate option, he or she will make equal monthly payments of $1,347 for 30 years.
To illustrate this more clearly, assume that the bank gives the borrower $300,000, 30-year loan with an introductory rate of 3.5% and a 5/1 ARM. The borrower will pay $1,347 monthly for the first five years. After that period, the remaining debt will be paid on fluctuating rates which will depend on the interest rates set by the benchmark indexes.
If the rates increase by 6%, for instance, the borrower will make monthly payments of $1,347. However, if the rates reduce by 3%, the borrower will pay $1,265. On the other hand, if the borrower opts for the fixed interest rate option, he or she will make equal monthly payments of $1,347 for 30 years.
How To Choose Between The Fixed And Variable Interest Rate
Ultimately, both the fixed and the variable interest rates can favor you depending on your specific situation, and thus the decision is based on personal preferences. You should, however, base your decision on all factors discussed here.| Variable rates are better when: | Fixed rates are better when: |
| You have a shorter loan term, which limits the chances for rates to change. | You have a longer loan term, and you don’t want to be affected by moving rates. |
| You can afford an increased minimum payment. | You don’t want your minimum payment to increase. |
| You know for sure that interest rates will decrease or stay flat in the near future. | You know for sure that interest rates will increase in the future and you want to lock in a rate now. |
- The value you keep on predictability and stability.
- Whether you plan to increase your monthly payments.
- Whether you will switch your loan plan in the future.
| Variable Rate | Fixed Rate | Semi-Fixed Rate |
| Suitable for a long tenure | Suitable for short/medium term | Suitable for medium-term |
| Ideal when the interest rate is expected to fall | Ideal when the interest rate is expected to rise | Ideal when the interest rate is expected to rise in the short-term and then fall |
| Opt for this scheme when income flow is adequate to service the rate fluctuation | Opt for this scheme when income flow is not expected to grow | Opt for this scheme when income flow is not expected to grow |
| Suited to loan borrowers who can take risks (for example, borrowers aged 30-35) | Suited to loan borrowers who do not want to take risks (for example, borrowers aged 50 years) | Suited to loan borrowers who do not want to take risks |
Customer Notice
We strive to provide accurate information regarding personal finance and debt management, but it may not apply to an individual’s situation directly. This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice. PayDayAllDay.com won’t bear any responsibility in relation to personal decisions made based on it. You should consult your financial or tax advisor before making any financial decisions.
References and Sources
1. Investopedia Staff. Fixed Interest Rate. Investopedia.com. Available at https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fixedinterestrate.asp
2. Matt Lee. Fixed and Variable Rate Loans: Which is Better? Investopedia.Com. Available at https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/07/fixed-variable.asp
3. Ask CFPB. What is the Difference Between a Fixed-Rate and Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM) Loan?. Consumerfinance.Gov. Available at https://www.consumerfinance.gov/ask-cfpb/what-is-the-difference-between-a-fixed-rate-and-adjustable-rate-mortgage-arm-loan-en-100/
4. FAQ. Does a Fixed-Rate Loan Option Make Sense for You? Bank of America Corporation. Available at https://www.bankofamerica.com/home-equity/fixed-rate-loan/
5. Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates: What’s the Difference? ValuePenguin Inc. Available at https://www.valuepenguin.com/loans/fixed-vs-variable-interest-rates
6. Statistics (2018). Historical Data on Selected Interest Rates (Daily) – H15. Federal Reserve System. Available at https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
7. Arisha Setalvad (2018). How to Choose Between a Fixed-Rate or Variable-Rate Student Loan. Credible.Com. Available at https://www.credible.com/blog/student-loans/choosing-fixed-or-variable-rate-student-loan/

Alice was born and raised in Compton, California. Then she studied at Yuin University, the place where she became passionate about researching the thin ropes between money and meaning. She is insatiably interested in people’s potential, wondering why some succeed and others don’t. Thus, the articles on her blog explore a multitude of seemingly unconnected things: money, psychology, entrepreneurship, creativity, spirituality, philanthropy, just to name a few.
